ABSTRACT
OBJECTIVE To estimate the impact of the 2015–2018 economic crisis on tobacco consumption in Brazil.
METHODS This is an interrupted time series analysis conducted with data from 27 cities collected by VIGITEL, using linear regression models to account for first-order autocorrelation. Analyses were conducted based on gender, age group, and education level.
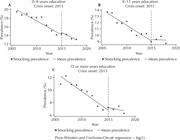
RESULTS Smoking rates decreased between 2006 and 2018, decelerating after the crisis onset. Differently than women, men showed an immediate but transient increase in smoking, followed by a decelerated decrease. Those over 65 also showed increased smoking rates immediately after the economic crisis onset, but decline accelerated later on. In turn, we found a trend reversal among those aged 31–44. Rates also decreased among those with lower education levels, but decelerated among those with more years of schooling.
CONCLUSION An economic crisis have varied impacts on the smoking habits of different population groups. Tobacco control policies should entail a detailed understanding of smoking epidemiology, especially during an economic crisis.
Tobacco Use Disorder, epidemiology; Poverty; Health Impact Assessment; Financial Management

 Smoking prevalence and economic crisis in Brazil
Smoking prevalence and economic crisis in Brazil Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail

